Table of Contents
ToggleWelcome to our journey through the intricate world of oxygen sensors, a vital yet often overlooked component of modern vehicle engines. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the role of oxygen sensors, their types, how they operate, and why they matter for your vehicle’s performance.
The importance of understanding oxygen sensors.
At the heart of every engine, a tiny but mighty device plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal engine performance and reducing harmful emissions. If you’ve ever wondered about the mysteries behind your vehicle’s efficient operation, you’re about to discover some answers.
In this blog post, we will explore everything you need to know about oxygen sensors, from their basic functionality to signs of malfunction and even tips for maintenance. So, fasten your seatbelts as we embark on a journey to unlock the secrets of oxygen sensors.
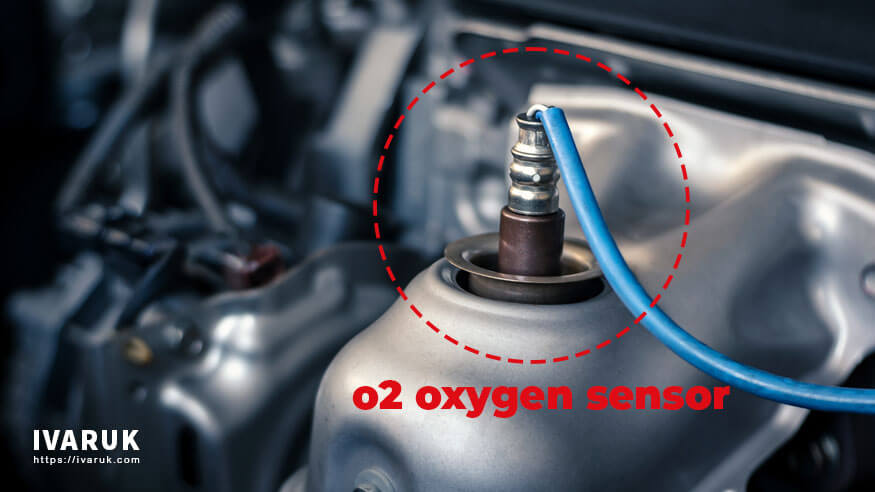

What Is an Oxygen Sensor?
Before we dive into the technical details, let’s start with the basics. What exactly is an oxygen sensor, and why is it so important for your vehicle?
An oxygen sensor, often referred to as an O2 sensor, is a small electronic device that monitors the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases of your vehicle. It is typically mounted in the exhaust system and plays a pivotal role in ensuring your engine runs efficiently while minimizing harmful emissions.
“Is your check engine light on? Trust IVARUK for expert car diagnostics and repair services. We’ll keep your ride running smoothly!”
The Importance of Oxygen Sensors in Modern Engines
In the early days of automobiles, engines operated with limited knowledge of the air-fuel mixture, resulting in less efficient combustion and increased pollution. However, the introduction of oxygen sensors revolutionized the automotive industry.
Oxygen sensors are the unsung heroes of modern engines, constantly providing feedback to the engine control unit (ECU) to fine-tune the air-fuel mixture. This real-time data allows engines to burn fuel more efficiently, which not only enhances performance but also reduces harmful emissions.
Imagine having a personal coach who adjusts your workout routine in real-time to maximize your strength and endurance. Oxygen sensors do precisely that for your engine, ensuring it operates at peak efficiency under various driving conditions.
Types of Oxygen Sensors
Oxygen sensors come in different types, each serving specific purposes in the engine management system. Here are the two primary types:
- Narrowband Oxygen Sensors (NBO2): These are the most common type of oxygen sensors found in vehicles. They operate with a narrow range of oxygen concentration and are primarily responsible for maintaining the air-fuel ratio around stoichiometric (ideal) levels.
- Wideband Oxygen Sensors (WBO2): Wideband sensors are more advanced and provide a broader range of oxygen concentration data. They are often used in performance and fuel-efficient vehicles to achieve precise air-fuel ratios.
Understanding these sensor types is essential because they influence how your engine adjusts its air-fuel mixture, affecting both performance and fuel efficiency.
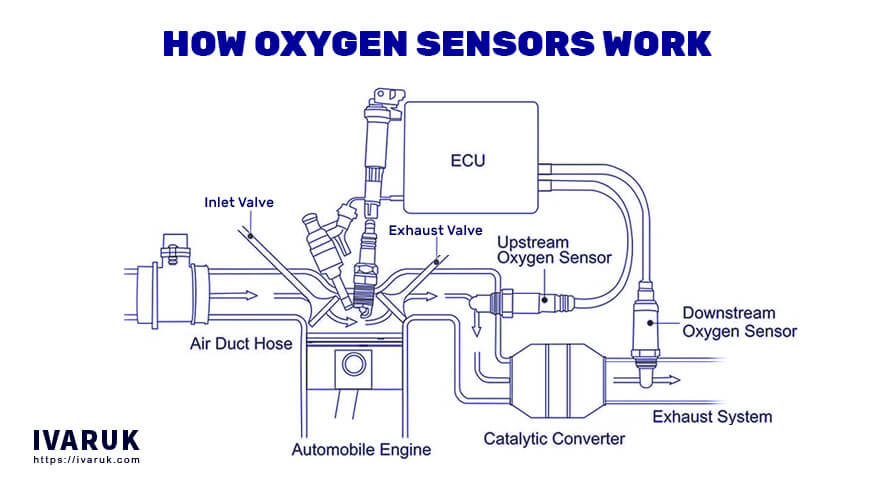
How Oxygen Sensors Work
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s dive into the fascinating inner workings of oxygen sensors. Understanding their operation will help you appreciate their importance.
Oxygen sensors operate on a simple principle: they measure the oxygen content in the exhaust gases and transmit this data to the ECU. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how they work:
- Exhaust Gas Sampling: The oxygen sensor is strategically placed in the exhaust system, allowing it to sample the exhaust gases.
- Oxygen Measurement: Inside the sensor, there are two chambers—one exposed to the exhaust gases and the other to ambient air. These chambers are separated by a special material known as an electrolyte. When the exhaust gases contain oxygen, a chemical reaction occurs at the sensor’s electrodes, generating voltage.
- Voltage Output: The voltage generated is directly proportional to the oxygen content in the exhaust. A high oxygen concentration results in low voltage, while a low oxygen concentration leads to high voltage.
- Data Transmission: The ECU receives the voltage signal from the oxygen sensor and interprets it as information about the air-fuel mixture’s richness or leanness.
By continuously monitoring this voltage, the ECU can make immediate adjustments to the fuel injection to maintain the ideal air-fuel ratio for efficient combustion. This dynamic process ensures that your engine runs smoothly and efficiently in various driving conditions.
“Unlock the Secrets of Oxygen Sensors with IVARUK’s Car Inspection and Repair Services! Our experts understand the vital role oxygen sensors play in your vehicle’s performance. We’ll diagnose, repair, and optimize your car’s engine, ensuring it runs efficiently. Drive smart, choose IVARUK for top-notch Car Inspection and Repair!” contact us!
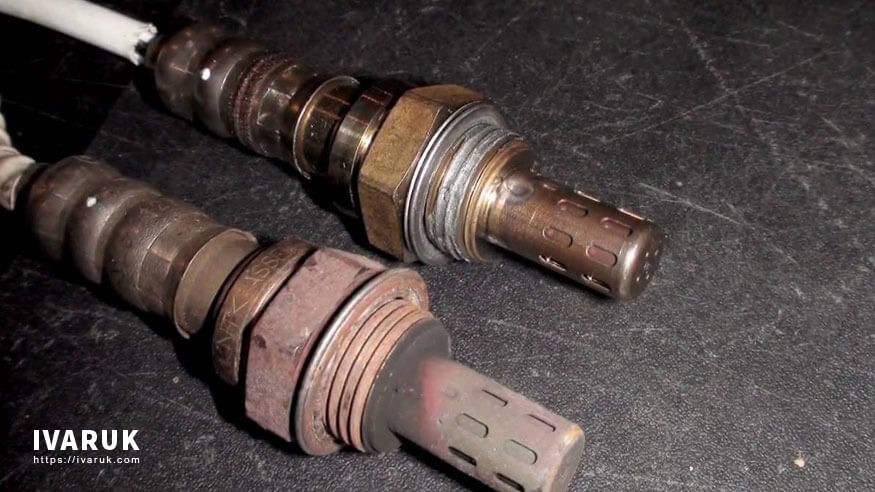

Signs of a Failing Oxygen Sensor
As with any mechanical or electronic component, oxygen sensors can deteriorate over time. Recognizing the signs of a failing oxygen sensor is essential for timely maintenance and preventing potential engine issues.
Here are some common indicators that your oxygen sensor may be malfunctioning:
- Check Engine Light (CEL): One of the most noticeable signs is the illumination of the check engine light on your dashboard. The ECU often triggers the CEL when it detects irregular data from the oxygen sensor.
- Decreased Fuel Efficiency: A failing oxygen sensor can lead to an incorrect air-fuel mixture, causing your engine to consume more fuel than necessary. If you notice a sudden drop in fuel efficiency, it’s worth investigating the sensor’s condition.
- Rough Idling: An unstable idling engine or engine stalling can be attributed to a malfunctioning oxygen sensor. The sensor’s inaccurate readings can disrupt the engine’s smooth operation.
- Increased Emissions: If your vehicle fails an emissions test or emits excessive pollutants, a faulty oxygen sensor could be to blame. Oxygen sensors play a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions, so any issue with them can result in environmental consequences.
- Poor Engine Performance: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can lead to reduced engine performance, including sluggish acceleration and reduced power output. This can be particularly noticeable when driving uphill or during overtaking.
Replacing Your Oxygen Sensor: DIY or Professional Service?
If you suspect that your oxygen sensor is failing based on the signs mentioned earlier, the next step is to address the issue promptly. The question is, should you attempt to replace it yourself or seek professional assistance?
While replacing an oxygen sensor is technically possible as a DIY project, it’s essential to consider your level of automotive expertise and access to the necessary tools. Here are some factors to consider:
Pros of DIY Replacement:
- Cost Savings: Replacing the sensor yourself can save you on labour costs.
- Learning Experience: If you enjoy DIY projects, it’s an opportunity to learn more about your vehicle’s components.
- Immediate Action: You can address the issue promptly if you have the required tools and know-how.
Cons of DIY Replacement:
- Technical Complexity: Replacing an oxygen sensor requires specific tools and a good understanding of your vehicle’s exhaust system.
- Error Risk: Incorrect installation can lead to further issues, such as damaging the threads in the exhaust manifold.
- Warranty Concerns: If your vehicle is under warranty, DIY replacement may void the warranty, so it’s crucial to check the terms.
Professional Service:
- Expertise: Certified technicians have the experience and equipment needed for precise sensor replacement.
- Warranty Protection: Professional service typically comes with a warranty, ensuring that the job is done correctly.
- Diagnostic Accuracy: Technicians can perform comprehensive diagnostics to ensure the oxygen sensor is the actual problem.
Before deciding, assess your comfort level with automotive work and the availability of tools. If in doubt, consulting a professional is the safest option to avoid potential complications.

Oxygen Sensor Maintenance Tips
Preventing oxygen sensor issues and prolonging their lifespan is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s efficiency. Here are some maintenance tips to consider:
- Use Quality Fuel: High-quality fuel can reduce the likelihood of sensor contamination, leading to longer sensor life.
- Regular Maintenance: Follow your vehicle’s recommended maintenance schedule, including oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug checks. A well-maintained engine is less likely to strain the oxygen sensor.
- Avoid Engine Modifications: Altering your vehicle’s engine performance, such as installing aftermarket exhaust systems, can impact the oxygen sensor’s accuracy.
- Check for Exhaust Leaks: Ensure there are no leaks in your exhaust system, as this can introduce unmeasured oxygen into the exhaust stream, affecting sensor readings.
- Keep the Engine Tuned: A well-tuned engine is less likely to produce excessive emissions that can damage the sensor.
The Role of Oxygen Sensors in Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a topic of increasing importance in today’s world, both for economic and environmental reasons. Oxygen sensors play a pivotal role in achieving optimal fuel efficiency by ensuring that your engine operates at its peak performance while consuming fuel judiciously.
Here’s how oxygen sensors contribute to improved fuel efficiency:
- Optimizing Air-Fuel Ratio: Oxygen sensors continuously monitor the air-fuel mixture and provide real-time feedback to the ECU. By maintaining a precise air-fuel ratio (usually around 14.7:1), the engine can burn fuel efficiently without waste. This balance prevents excess fuel from being injected into the engine, reducing fuel consumption.
- Adapting to Driving Conditions: Your driving conditions can vary significantly, from cruising on the highway to stop-and-go city traffic. Oxygen sensors ensure that the engine adjusts to these conditions by fine-tuning the air-fuel mixture accordingly. This adaptability prevents unnecessary fuel consumption during idling or aggressive acceleration.
- Reducing Fuel Waste: Without oxygen sensors, engines would rely on fixed air-fuel ratios, leading to inefficient combustion. This inefficiency results in fuel waste and higher emissions. Oxygen sensors help engines achieve the right mixture for complete fuel combustion, minimizing waste.
- Enhancing Combustion Efficiency: When the air-fuel mixture is optimal, combustion efficiency is maximized. This means that more of the fuel’s energy is converted into useful work, such as propelling your vehicle forward. Improved combustion efficiency directly translates to better fuel economy.
- Lowering Harmful Emissions: Achieving fuel efficiency also means producing fewer harmful emissions. Oxygen sensors ensure that the engine’s emissions are within acceptable limits, contributing to a cleaner environment.
By maintaining the delicate balance between air and fuel, oxygen sensors enable your engine to operate with precision, ultimately saving you money at the pump and reducing your carbon footprint.
The Role of Oxygen Sensors in Reducing Emissions
In an era where environmental concerns are paramount, the role of oxygen sensors in reducing harmful emissions cannot be overstated. These sensors are instrumental in helping vehicles meet strict emission standards and minimizing their impact on the planet.
Here’s how oxygen sensors contribute to reducing emissions:
- Monitoring Emissions: Oxygen sensors continuously monitor exhaust gases, detecting the presence of pollutants such as carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), and nitrogen oxides (NOx). When these pollutants exceed acceptable levels, the ECU makes adjustments to reduce emissions.
- Catalytic Converter Efficiency: Oxygen sensors are closely linked to the performance of the catalytic converter, another critical component in emission control. The converter relies on accurate oxygen sensor data to facilitate chemical reactions that convert harmful gases into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
- Real-time Adjustments: In situations where engine conditions result in higher emissions, such as during cold starts or heavy acceleration, oxygen sensors provide immediate feedback to the ECU. This prompts the ECU to make adjustments, such as increasing fuel injection or altering ignition timing, to reduce emissions.
- Compliance with Emission Standards: Governments worldwide enforce strict emission standards to combat air pollution. Oxygen sensors are a crucial part of ensuring that vehicles comply with these standards, allowing for cleaner air and a healthier environment.
In essence, oxygen sensors are the guardians of our environment, working diligently to minimize the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. By doing so, they play a significant role in making our roads and cities more environmentally friendly.

The Future of Oxygen Sensors in Automotive Technology
As technology advances at a rapid pace, the automotive industry is no exception to the wave of innovation sweeping across various sectors. Oxygen sensors, being integral to engine management and emissions control, are also evolving to meet the demands of a changing automotive landscape.
Here’s a glimpse into the future of oxygen sensors:
- Advanced Sensor Types: While traditional narrowband and wideband oxygen sensors have served well, future vehicles may incorporate even more advanced sensor types. These sensors could provide even finer control over the air-fuel mixture, leading to higher efficiency and lower emissions.
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning: As vehicles become more connected and intelligent, oxygen sensors could be integrated with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning systems. This would enable real-time, adaptive adjustments to optimize engine performance and emissions under a wide range of driving conditions.
- Sensor Miniaturization: Smaller, more compact sensors could become commonplace, allowing for easier integration into various parts of the exhaust system. This could lead to improved sensor placement and even more accurate readings.
- Hybrid and Electric Vehicles: The rise of hybrid and electric vehicles presents new challenges and opportunities for oxygen sensors. While traditional internal combustion engines still rely on these sensors, electric vehicles may use them in different ways to monitor other aspects of vehicle performance, such as battery efficiency.
- Environmental Sensors: Future vehicles may incorporate a broader array of environmental sensors, including those for detecting particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and other pollutants. These sensors would work in conjunction with oxygen sensors to provide a more comprehensive picture of emissions and environmental impact.
- IoT Connectivity: The Internet of Things (IoT) is making its way into vehicles, and oxygen sensors could be part of this connectivity trend. Sensors may transmit data to a central vehicle management system or even to cloud-based platforms for analysis and diagnostics.
- Emission Reduction Technologies: Oxygen sensors will continue to play a pivotal role in emerging emission reduction technologies, such as selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems. These technologies rely on precise sensor data to reduce harmful emissions further.
Conclusion
Our journey through the world of oxygen sensors has shed light on their indispensable role in modern vehicles. From optimizing engine performance to reducing emissions, these small yet sophisticated devices have a significant impact on both your vehicle’s efficiency and the environment.
As we look to the future, we can anticipate exciting developments in oxygen sensor technology, further enhancing their ability to drive cleaner, more efficient vehicles. Whether you’re a car enthusiast or simply someone who cares about the air we breathe, understanding the role of oxygen sensors in automotive technology is essential.
Next time you start your car and hit the road, remember that there’s a tiny but mighty hero under the hood—your oxygen sensor—working tirelessly to ensure a smooth and eco-friendly journey. It’s a testament to the power of innovation and engineering in making our world a better place, one engine revolution at a time.
Thank you for joining us on this exploration of oxygen sensors. We hope you’ve gained valuable insights into their significance and the promising future that lies ahead for these essential automotive components. Safe travels and a cleaner, more efficient road ahead!
What happens if I don’t replace a failing oxygen sensor?
Neglecting to replace a failing oxygen sensor can lead to reduced fuel efficiency, increased emissions, poor engine performance, and potential damage to the catalytic converter.
Questions about the oxygen sensor
- How often should oxygen sensors be replaced?
Oxygen sensors typically have a lifespan of 50,000 to 100,000 miles, but it’s essential to follow your vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations for replacement intervals.
- Can a faulty oxygen sensor cause my vehicle to fail an emissions test?
Yes, a malfunctioning oxygen sensor can lead to elevated emissions, which may cause your vehicle to fail an emissions test.
- Are oxygen sensors covered by warranty?
Oxygen sensor warranties can vary depending on the manufacturer and the specific sensor. Check your vehicle’s warranty documentation for details.
- Can I drive with a malfunctioning oxygen sensor?
While it’s possible to drive with a faulty sensor, it’s not recommended. Doing so can lead to decreased fuel efficiency, increased emissions, and potential engine damage over time.
- How can I prevent oxygen sensor issues?
Regular maintenance, using high-quality fuel, and avoiding engine modifications can help prevent oxygen sensor problems.
- Are there aftermarket oxygen sensors available?
Yes, there are aftermarket oxygen sensors available, but it’s crucial to choose high-quality sensors that meet your vehicle’s specifications.
- Do all vehicles have oxygen sensors?
Most modern vehicles, especially those manufactured after the mid-1980s, are equipped with oxygen sensors to monitor and optimize engine performance and emissions.




One Response
I read the OXYGEN SENSORS article. There is complete information in this article that I did not know. that was perfect.